Showing posts with label executing a project. Show all posts
Showing posts with label executing a project. Show all posts
Sunday, December 18, 2011
Chapter 40: Summary - Project Management Process Groups
Not all project management processes apply to all projects or project phases. Process groups can overlap and interact. Forty-two project management processes are contained within the five project management process groups:
1. Initiating
2. Planning
3. Executing
4. Monitoring and controlling
5. Closing
Initiating Process Group
The Initiating Process Group Formally authorizes new project or project phase. The two processes in it are:
1. Develop project charter - Authorizing project or project phase. The project charter defines the project’s purpose, identifies objectives, and authorizes the project manager to start the project.
2. Identify stakeholders - Documents all of the people or organizations that have an interest in the outcome of the project and their level of interest, impact, and involvement.
Planning Process Group
The Planning Process Group Defines objectives and plans course of action required to meet objectives and project scope. It also facilitates project planning across process groups. The Processes in the Planning Process Group are:
1. Develop project management plan - Primary source for how project is planned, executed, monitored, controlled, and closed. It’s an iterative and ongoing process often resulting in changes to the project management plan. This progressive detailing is called rolling wave planning.
2. Collect requirements - Documenting the stakeholders’ needs to meet the project objectives.
3. Define scope - Developing a detailed project scope.
4. Create WBS - Subdividing major project deliverables and project work into smaller, more manageable components.
5. Define activities - Identifying specific activities to be performed to produce project deliverables.
6. Sequence activities - Identifying and documenting dependencies among schedule activities.
7. Estimate activity resources - Type and quantity of resources required to perform each schedule activity.
8. Estimate activity durations - Number of work periods needed to complete individual schedule activities.
9. Develop schedule - Analyzing activity sequences, durations, resource requirements, and schedule constraints to create project schedule.
10. Estimate costs - Developing approximation of costs of resources needed to complete project activities.
11. Determine budget - Aggregating estimated costs of individual activities to establish cost baseline.
12. Plan quality - Identifying relevant quality standards and determining how to satisfy them.
13. Develop human resource plan - Identifying and documenting project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships.
14. Plan communications - Determining stakeholder communication needs.
15. Plan risk management - Deciding how to approach, plan, and execute risk management activities.
16. Identify risks - Determining which risks might affect the project and documenting their characteristics.
17. Perform qualitative risk analysis - Prioritizing risks for subsequent further analysis by assessing and combining their probabilities of occurrence and impacts.
18. Perform quantitative risk analysis - Numerically analyzing the effect on project objectives of identified risks.
19. Plan risk responses - Developing options to enhance opportunities and reduce threats to project objectives.
20. Plan procurements - Documenting products, services, and results requirements and identifying potential sellers.
Executing Process Group
The Executing Process Group Integrates resources to carry out project management plan. The processes in this group are
1. Direct and manage project execution - Directing technical and organization interfaces to execute work defined in project management plan.
2. Perform quality assurance - Applying planned, systematic quality activities to ensure project employs processes needed to meet requirements.
3. Acquire project team - Obtaining human resources needed to complete project.
4. Develop project team - Development improves competencies and interaction of team members.
5. Manage project team - Tracking team member performance, providing feedback, resolving issues, and coordinating changes to enhance project performance.
6. Distribute information - Providing information to stakeholders in a timely manner.
7. Manage stakeholder expectations - Managing stakeholder expectations to satisfy their requirements and resolve issues.
8. Conduct procurements - Obtaining seller responses, selecting sellers, and awarding contracts.
Monitoring and Controlling Process Group
The Monitoring & Controlling Process Group Monitors progress to identify variances from the project management plan so corrective action can be taken to meet project objectives. The processes in this group are:
1. Monitor and control project work - Collecting, measuring, and disseminating performance information and assessing measurements and trends to affect process improvements. Includes risk monitoring to ensure risks are identified early, their statuses reported, and risk plans executed. Monitoring includes status reporting, progress measurement, and forecasting.
2. Perform integrated change control - Ensure changes are beneficial; determine whether a change has occurred; and manage approved changes, including when they occur. Performed throughout project life cycle.
3. Verify scope - Acceptance of completed project deliverables.
4. Control scope - Controlling changes to project scope.
5. Control schedule - Controlling changes to project schedule.
6. Control costs - Influencing factors that create variances and controlling changes to project budget.
7. Perform quality control - Monitoring project results to determine compliance with quality standards and identifying ways to eliminate unsatisfactory performance.
8. Report performance - Collecting and distributing performance information, including status reporting, progress measurement, and forecasting.
9. Monitor and control risks - Tracking identified risks, monitoring risks, identifying new risks, executing risk response plans, and evaluating their effectiveness throughout the project life cycle.
10. Administer procurements - Managing contract between buyer and seller, reviewing and documenting seller performance, and managing contractual relationship with outside buyer of project.
Closing Process Group
The Closing Process Group Formalizes acceptance of product, service, or result and brings project or project phase to an end. The processes in this group are:
1. Close project or phase - Finalizing all activities across process groups to formally close project or project phase.
2. Close procurements - Completing each procurement, including resolution of open items, and closing each procurement relevant to project or project phase.
Prev: Chapter 39
Next: Chapter 41
Friday, July 1, 2011
Summary - Managing Project Work
Let us summarize the important points we learnt in the previous set of Chapters on Project Execution.
• The project management plan is executed using the processes in the executing process group.
• The high-level umbrella process in this group is the Direct and Manage Project Execution process, whose main goal is to produce the project deliverables.
• A significant task to perform during project execution is quality assurance, which involves auditing the results from quality control measurements to ensure that quality requirements are being met.
• Due to a lack of resources in the performing organization, you might need to obtain some products, services, or results from outside the project team to complete the project. This is called procurement.
• The Conduct Procurements process is used to implement the procurement plan, which involves obtaining seller responses, selecting sellers based on the responses, and reaching an agreement with the selected sellers, such as a contract to obtain (procure) the products, services, or results.
Prev: Conducting Procurements
Next: Important Terms & Definitions - Managing Project Work
• The project management plan is executed using the processes in the executing process group.
• The high-level umbrella process in this group is the Direct and Manage Project Execution process, whose main goal is to produce the project deliverables.
• A significant task to perform during project execution is quality assurance, which involves auditing the results from quality control measurements to ensure that quality requirements are being met.
• Due to a lack of resources in the performing organization, you might need to obtain some products, services, or results from outside the project team to complete the project. This is called procurement.
• The Conduct Procurements process is used to implement the procurement plan, which involves obtaining seller responses, selecting sellers based on the responses, and reaching an agreement with the selected sellers, such as a contract to obtain (procure) the products, services, or results.
Prev: Conducting Procurements
Next: Important Terms & Definitions - Managing Project Work
Chapter 58: Executing a Project: Big Picture
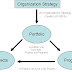
The project work defined in the project management plan is executed by using the processes in the executing process group. The high level idea of the whole process can be understood by studying the picture below:
As I said earlier, it is up to the project team to determine which of these processes is relevant for the project that is currently being executed. The processes in this group are used to accomplish a three-pronged goal:
The following list defines the processes shown in the picture above.
• Direct and manage project execution - Manage various interfaces in the project execution to complete the project work smoothly in order to produce the project outcome, such as deliverables and objectives.
• Acquire project team - Obtain the project team members needed to perform the project work. (You need people to do the work right?)
• Develop project team - Improve the competencies of team members and interaction among team members to enhance project performance.
• Manage project team - Manage the project team, which includes tracking the performance of team members, providing feedback, resolving issues, and managing changes to improve project performance. (A Well Managed Team is an efficient team.)
• Perform quality assurance - Audit the results from the quality control measurements to ensure that the quality requirements are being met.
• Distribute information - Make the relevant information about the project, such as project progress, available to the stakeholders according to the communication management plan.
• Conduct procurements - Obtain responses from potential sellers in terms of quotes, bids, offers, and proposals for their product or services needed for the project; select sellers; and negotiate written contracts with the selected sellers.
• Manage stakeholder expectations - Stay on the same page with the stakeholders by communicating and working with them on their needs and issues.
Prev: Introduction to Project Execution
Next: Directing & Managing Project Execution
As I said earlier, it is up to the project team to determine which of these processes is relevant for the project that is currently being executed. The processes in this group are used to accomplish a three-pronged goal:
• Coordinate people and resources used to perform the project activities
• Integrate and manage the project activities being performed
• Ensure the implementation of the project scope and approved changes
The following list defines the processes shown in the picture above.
• Direct and manage project execution - Manage various interfaces in the project execution to complete the project work smoothly in order to produce the project outcome, such as deliverables and objectives.
• Acquire project team - Obtain the project team members needed to perform the project work. (You need people to do the work right?)
• Develop project team - Improve the competencies of team members and interaction among team members to enhance project performance.
• Manage project team - Manage the project team, which includes tracking the performance of team members, providing feedback, resolving issues, and managing changes to improve project performance. (A Well Managed Team is an efficient team.)
• Perform quality assurance - Audit the results from the quality control measurements to ensure that the quality requirements are being met.
• Distribute information - Make the relevant information about the project, such as project progress, available to the stakeholders according to the communication management plan.
• Conduct procurements - Obtain responses from potential sellers in terms of quotes, bids, offers, and proposals for their product or services needed for the project; select sellers; and negotiate written contracts with the selected sellers.
• Manage stakeholder expectations - Stay on the same page with the stakeholders by communicating and working with them on their needs and issues.
Prev: Introduction to Project Execution
Next: Directing & Managing Project Execution
Chapter 57: Introduction to Project Execution Phase
Well, before we begin, let me congratulate you on completing two big sections on learning for the PMP Certification, “Initiating a Project” and “Planning a Project”. Each section involved multiple chapters and we are now entering the Project Entering Phase. This chapter is just an introduction to the whole project execution phase.
So, lets get started!!!
What is Project Execution Phase?
After a project has been planned using the processes in the planning process group, it needs to be executed using the processes in the executing process group. The project team determines which of the processes in the executing process group are relevant to the project at hand. The goal of the execution stage is to complete the project work specified in the project management plan to meet the project requirements. To accomplish that, you will need to acquire, develop, and manage the project team. Your organization might not have the resources to finish certain parts of this work. You will need to use procurement for those parts of the work. You also need to ensure that all the planned quality activities are performed. This is accomplished by using the quality assurance process.
Directing and managing project execution is the process of implementing the project management plan developed during project planning. The end product of this process is the project deliverables. This is a high-level umbrella process under which other execution processes are performed, such as assuring quality and conducting procurements. So the core question in this section is how to execute a project as planned.
Well my friend, this is what we are going to learn in the subsequent chapters.
Prev: Important Terms - Planning for Quality & Risk Management
Next: Executing a Project - Big Picture
So, lets get started!!!
What is Project Execution Phase?
After a project has been planned using the processes in the planning process group, it needs to be executed using the processes in the executing process group. The project team determines which of the processes in the executing process group are relevant to the project at hand. The goal of the execution stage is to complete the project work specified in the project management plan to meet the project requirements. To accomplish that, you will need to acquire, develop, and manage the project team. Your organization might not have the resources to finish certain parts of this work. You will need to use procurement for those parts of the work. You also need to ensure that all the planned quality activities are performed. This is accomplished by using the quality assurance process.
Directing and managing project execution is the process of implementing the project management plan developed during project planning. The end product of this process is the project deliverables. This is a high-level umbrella process under which other execution processes are performed, such as assuring quality and conducting procurements. So the core question in this section is how to execute a project as planned.
Well my friend, this is what we are going to learn in the subsequent chapters.
Prev: Important Terms - Planning for Quality & Risk Management
Next: Executing a Project - Big Picture
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
© 2013 by www.getpmpcertified.blogspot.com. All rights reserved. No part of this blog or its contents may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior written permission of the Author.
Followers
Popular Posts
-
So far, we have been talking in terms of projects only. There are two other terms that are closed linked with projects and project manageme...
-
In the previous chapter, we saw how to create the Project Scope Document. The next step in planning for a projects scope is to create the Wo...
-
In the previous chapter, we saw the project lifecycle in detail. In this chapter, we are going to take a look at the Project Management Kno...
-
In the previous chapter , we took a look at Expected Monetary Value or EMV Analysis . The Decision Tree Analysis is another tool/technique ...
-
In the previous chapter we learnt how to create the project human resource plan. To get resources you need to spend money (Cost) and you can...
-
In the previous chapter , we learnt the basic details about Continuous Distributions. In this chapter, we are going to take a detailed look...
-
In the previous chapter we learnt that the risk register is going to be constantly updated as we progress through the various processes in...
-
Expected Monetary Value Analysis or EMV Analysis in short is the 2nd tool and technique in the Quantitative Risk Analysis and Modeling Tech...
-
In the previous chapter, we saw that an organizations policies and culture can have a significant impact on a project. Towards the end we al...
-
In the previous chapter, we took a look at how to sequence the activities based on the requirements and dependencies. The next step would be...