Let us wrap up the Project Scope Planning topic by reviewing the important terms and definitions we have learnt as part of this topic.
• Alternatives identification - A technique used to apply nonstandard approaches, such as brainstorming and lateral thinking, to perform project work.
• Baseline - A reference plan for components, such as schedule, scope, and cost, against which performance deviations are measured. The reference plan can be the original or the modified plan.
• Brainstorming - A creative technique generally used in a group environment to gather ideas as candidates for a solution to a problem or an issue without any immediate evaluation of these ideas. The evaluation and analysis of these ideas happens later.
• Code of accounts - A numbering system used to uniquely identify each component of a WBS.
• Configuration management - Refers to controlling the characteristics of a product, a service, or a result of a project. It includes documenting the features of a product or a service, controlling and documenting changes to the features, and providing support for auditing the products for conformance to requirements.
• Control account - A node in the WBS that acts as a management control point where scope, schedule, and actual cost are integrated and compared to the earned value to measure the project performance.
• Decomposition - A planning technique to subdivide the project scope, including deliverables, into smaller, manageable tasks called work packages.
• Deliverable - A unique and verifiable product, a capability to provide a service, or a result that must be produced to complete a project or a process or phase of the project.
• Lateral thinking - Thinking outside the box, beyond the realm of your experience, to search for new solutions and methods, rather than only better uses of the current solutions and methods.
• Planning package - A WBS component that is below the control account that has a well-defined work content but does not yet have a detailed schedule.
• Product scope - Features and functions that characterize a product, service, or result to be delivered by the project.
• Project management plan - An approved document that describes how the project will be executed, monitored and controlled, and closed.
• Project scope - The work that must be performed (and only that work) to deliver products, services, or results with specified features that were promised by the project. The project scope draws the boundaries around the project—what is included and what is not.
• Project scope statement - A document that defines the scope of a project by stating what needs to be accomplished by the project.
• Requirement - A condition, characteristic, or capability that a specific outcome of the project must have.
• Rolling wave planning - A case of progressive elaboration in which the deliverables about which full information is available are decomposed to the lowest level, whereas the deliverables for which full information is not available are left at higher levels until the information becomes available.
• Scope baseline - The reference scope against which all the scope deviations are measured. It consists of the scope statement, the WBS document, and the WBS dictionary.
• Scope definition - The process used to develop the detailed project scope statement.
• Scope planning - The process of developing the project scope management plan.
• Subprojects - Parts of the main projects that are independent enough that each can be performed by separate project teams.
• Work breakdown structure (WBS) - A deliverable-oriented hierarchical structure that displays the decomposition of deliverables into work, which must be performed to accomplish the project objectives and create the project deliverables.
• Work package - A deliverable or a task at the lowest level of each branch of the WBS.
Previous: Summary - Project Scope Planning
Next: Introduction to Project Schedule
Showing posts with label work breakdown structure. Show all posts
Showing posts with label work breakdown structure. Show all posts
Monday, May 16, 2011
Summary - Project Scope Planning
In the previous chapters, we have successfully completed the Project Scope Planning section of Project Planning. Let us quickly summarize the key points we learnt in this topic.
• After a project has been initiated, the project management plan is developed to specify how the project at hand will be executed, monitored & controlled, and closed.
• The project management plan can contain subsidiary plans, such as a quality management plan, a risk management plan, a project scope management plan, and a scope baseline.
• The scope baseline consists of the project scope statement, work breakdown structure (WBS), and WBS dictionary.
• Collecting requirements is part of the scope planning, which creates requirements documentation.
• The project charter and requirements documentation are used to define the scope, which creates the project scope statement.
• The project scope statement is a document that defines the scope of a project, including the product scope, by stating what needs to be accomplished by the project.
• It includes project deliverables, product description, product acceptance criteria, assumptions and constraints, and project exclusions.
• The project scope statement and requirements documentation are input items to creating the work breakdown structure (WBS), which is a breakdown of project deliverables into manageable pieces called work packages, which in turn are used to develop the project schedule.
• The WBS is supported by another document called the WBS dictionary, which offers details for the WBS components.
• The scope statement, the WBS document, and the WBS dictionary combined constitute the scope baseline against which all change requests are evaluated.
• The WBS is the heart of project management, as it is used in managing many aspects of the project, including developing the schedule.
Previous: Before & After WBS
Next: Important Terms - Project Scope Planning
• After a project has been initiated, the project management plan is developed to specify how the project at hand will be executed, monitored & controlled, and closed.
• The project management plan can contain subsidiary plans, such as a quality management plan, a risk management plan, a project scope management plan, and a scope baseline.
• The scope baseline consists of the project scope statement, work breakdown structure (WBS), and WBS dictionary.
• Collecting requirements is part of the scope planning, which creates requirements documentation.
• The project charter and requirements documentation are used to define the scope, which creates the project scope statement.
• The project scope statement is a document that defines the scope of a project, including the product scope, by stating what needs to be accomplished by the project.
• It includes project deliverables, product description, product acceptance criteria, assumptions and constraints, and project exclusions.
• The project scope statement and requirements documentation are input items to creating the work breakdown structure (WBS), which is a breakdown of project deliverables into manageable pieces called work packages, which in turn are used to develop the project schedule.
• The WBS is supported by another document called the WBS dictionary, which offers details for the WBS components.
• The scope statement, the WBS document, and the WBS dictionary combined constitute the scope baseline against which all change requests are evaluated.
• The WBS is the heart of project management, as it is used in managing many aspects of the project, including developing the schedule.
Previous: Before & After WBS
Next: Important Terms - Project Scope Planning
Chapter 32: Before and After the WBS
In the previous chapter, we saw how to create the WBS. Since the WBS is an important artifact, it would be better if we take a look at it with some more details.
So, lets get started!!!
Creating the WBS:
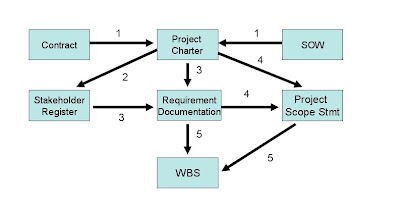
Even though we looked at how to create the WBS in great detail, it would make it easier for you to understand the whole process if we have another picture to explain it. Below is a picture that explains how the WBS is created.
In the picture above, each of the boxes is a document/artifact and arrows indicate the direction in which data flows. The numbers indicate the order in which data flows. For ex: The contract and the SOW are inputs to create the Project Charter. Similarly the Project Charter is an input to create the Stakeholder Register and these two together are inputs to the Requirement Documentation step and so on.
The WBS is at the heart of project management. It affects directly or indirectly almost all the processes that are performed after its creation.
Processes Based on the WBS:
As part of managing the project, there are many processes that are directly based on the WBS as part of the Scope Baseline. They are:
1. Cost Estimation
2. Quality Planning
3. Risk Identification
4. Procurement Planning
5. Defining Activities for Project Schedule
6. Budget Determination
Let us look at a diagram to understand this better.
The three most important things you need to understand about Project Scope Planning are:
• You need to collect requirements by using the Collect Requirements process before you can define the project scope.
• The requirements documentation generated by the Collect Requirements process and the project charter generated during the project initiation are used to define the scope, which is documented in the project scope statement.
• The requirements documentation and the project scope statement are input items to create the work breakdown structure (WBS), which is a breakdown of project deliverables into manageable pieces called work packages. The WBS is supported by another document called the WBS dictionary, which offers details for the WBS components.
Previous: Creating the WBS
Next: Summary - Project Scope Planning
So, lets get started!!!
Creating the WBS:
Even though we looked at how to create the WBS in great detail, it would make it easier for you to understand the whole process if we have another picture to explain it. Below is a picture that explains how the WBS is created.
In the picture above, each of the boxes is a document/artifact and arrows indicate the direction in which data flows. The numbers indicate the order in which data flows. For ex: The contract and the SOW are inputs to create the Project Charter. Similarly the Project Charter is an input to create the Stakeholder Register and these two together are inputs to the Requirement Documentation step and so on.
The WBS is at the heart of project management. It affects directly or indirectly almost all the processes that are performed after its creation.
Processes Based on the WBS:
As part of managing the project, there are many processes that are directly based on the WBS as part of the Scope Baseline. They are:
1. Cost Estimation
2. Quality Planning
3. Risk Identification
4. Procurement Planning
5. Defining Activities for Project Schedule
6. Budget Determination
Let us look at a diagram to understand this better.
The three most important things you need to understand about Project Scope Planning are:
• You need to collect requirements by using the Collect Requirements process before you can define the project scope.
• The requirements documentation generated by the Collect Requirements process and the project charter generated during the project initiation are used to define the scope, which is documented in the project scope statement.
• The requirements documentation and the project scope statement are input items to create the work breakdown structure (WBS), which is a breakdown of project deliverables into manageable pieces called work packages. The WBS is supported by another document called the WBS dictionary, which offers details for the WBS components.
Previous: Creating the WBS
Next: Summary - Project Scope Planning
Chapter 31: Creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
In the previous chapter, we saw how to create the Project Scope Document. The next step in planning for a projects scope is to create the Work Breakdown Structure or WBS. This is what we are going to look in this chapter.
So, lets get started!!!
What is WBS?
WBS stands for Work Breakdown Structure. It is something that helps breakdown the whole projects scope into smaller and more manageable pieces. This is also a very important process in project management. To be able to actually execute the project, the project scope is broken down into manageable tasks by creating a work breakdown structure (WBS). In other words, a WBS is a deliverable-oriented hierarchy of the work that must be performed to accomplish the objectives of and create the deliverables for the project.
How to create the WBS?
Just like other documents related to project planning & management, the WBS is created using a set of inputs, by applying a set of tools & techniques to create the WBS. The picture below is a high level summary of how the WBS is created.
The project scope statement contains the list of deliverables and the product description. The requirements documentation describes the product and project requirements. Information in these two items provides the basis for creating the WBS. You should always consider organizational process assets while going through this and several other processes. In this case, the organizational policies and procedure related to creating the WBS, as well as relevant project files and lessons learned from previous projects, are some examples of organizational process assets that can be helpful.
Furthermore, even though each project is unique, there are similarities among sets of projects in an organization. These similarities can be used to prepare templates that will be used as a starting point for the WBS, to avoid the duplication of work. With or without templates, you will need to go through breaking down the deliverables, a very important step in creating the WBS.
Decomposition
Decomposition is a technique used for subdividing the project deliverables into smaller, manageable tasks called work packages. The WBS is a hierarchical structure with work packages at the lowest level of each branch. Based on their complexity, different deliverables can have different levels of decomposition.
To understand Decomposition better, let us take a look at an example WBS of a Website Development Project
In any WBS – the lines are called “Branches” and the boxes are called “Nodes”. For practical understanding purposes, each of these nodes can be considered as one manageable piece of work.
As you can see, we have decomposed the whole project work into 3 parts:
1. User Interfaces
2. Server &
3. Database
Each of these parts is further divided into more nodes which carry out a specific function that is part of the higher level activity.
How do you decompose a Project Work?
You can decompose the project work by executing the following steps:
1. Identify the deliverables and the work involved by analyzing the project scope statement and the requirements documentation.
2. Understand the relationships among the deliverables.
3. Structure and organize the first level (Server, UI and Db in our example) of the WBS hierarchy. Based on the project at hand, you can use one of the following approaches:
o Use the deliverables as the components in the first level.
o Use the phases of the project as the components in the first level.
o Use the subprojects as components in the first level. A subproject is a part of the project that is independent enough of the rest of the project that it can be performed by another project team. This approach is useful when you want to outsource parts of the project.
o Use different approaches within each branch of the WBS, for example, a subproject and deliverables in the first level.
4. Decompose the upper level into more detailed components for the lower level.
5. Keep decomposing to lower levels until necessary and sufficient decomposition has been achieved.
6. Assign identification codes to the WBS components.
During decomposition, the components are defined in terms of how the project work will actually be executed and controlled. You must verify the correctness of the decomposition at each level by verifying that the lower-level components are necessary and sufficient for the completion of the corresponding higher-level deliverables.
Output of Creating WBS
The output of the Create WBS process consists of the following items:
Work breakdown structure
As explained earlier, the WBS is a deliverable-oriented hierarchical structure that decomposes the deliverables into the work that will be executed by the project team to create the planned deliverables and to accomplish the planned project objectives. The project manager creates this document with the help of the project team. Following are some important characteristics of the WBS:
• Control account - Remember that each node represents a deliverable or a component of it at certain level, and each deliverable will have scope, schedule, and cost attached to it. Some suitable nodes in the WBS are selected as management control points. At each of these control points, scope, schedule, and cost are integrated for the purposes of monitoring and controlling the performance. For example, the integrated scope, schedule, and actual cost at these points can be compared to the earned value to measure the project performance. Such management points are called control accounts. Each control account may have one or more work packages under it. Obviously, each work package must belong to only one account; otherwise, some factors, such as cost, will be double counted or counted multiple times. A WBS component that is below the control account, that has a well-defined work content but does not yet have a detailed schedule, is called a planning package.
• Code of account - Each component in the WBS hierarchy, including work packages, is assigned a unique identifier called a code of account identifier. These identifiers can then be used in estimating costs, scheduling, and assigning resources.
• Scope - The WBS embraces the full scope of the project. If a task is not included in the WBS, it will not be done as a part of the project.
• Step toward team building - Because the project manager creates the WBS with the help of the project team, it is also the beginning of the team-building process on the part of the project manager.
• Step toward scheduling - The WBS decomposes the project work into manageable pieces that can be assigned to individuals. This helps define the responsibilities for the team members and is the starting point for building the schedule.
• Reference for communication - Throughout the project, the WBS works as a reference for communication regarding what is included in the project and what is not.
WBS dictionary
This is a supporting document for the main WBS document to provide details about the components of the WBS. The details about a component might include elements such as a code of account identifier, description of work involved, quality requirements, acceptance criteria, a list of milestones schedule, cost estimates, required resources, contract information, and the organization or group responsible for this component.
Updates
During the create WBS process, the project team might realize that something out of the existing scope must be included in order to accomplish something in the scope. This will give rise to a change request, which might also come from other stakeholders during or after the first creation of the WBS. After the change request has been approved, not only the WBS will be changed—the scope statement must also be updated accordingly. The impact of the approved change request on the project scope management plan must be evaluated, and the plan must be updated accordingly.
Scope baseline
This is not a different item in and of itself. The scope statement, the WBS document, and the WBS dictionary combined constitute the scope baseline against which all the change requests will be evaluated.
A Last Word:
You might be wondering who creates the WBS. Well, as expected, it is your responsibility, and you, the project manager have to create it with the help of your team.
Previous: Defining Project Scope
Next: Before & After the WBS
So, lets get started!!!
What is WBS?
WBS stands for Work Breakdown Structure. It is something that helps breakdown the whole projects scope into smaller and more manageable pieces. This is also a very important process in project management. To be able to actually execute the project, the project scope is broken down into manageable tasks by creating a work breakdown structure (WBS). In other words, a WBS is a deliverable-oriented hierarchy of the work that must be performed to accomplish the objectives of and create the deliverables for the project.
How to create the WBS?
Just like other documents related to project planning & management, the WBS is created using a set of inputs, by applying a set of tools & techniques to create the WBS. The picture below is a high level summary of how the WBS is created.
The project scope statement contains the list of deliverables and the product description. The requirements documentation describes the product and project requirements. Information in these two items provides the basis for creating the WBS. You should always consider organizational process assets while going through this and several other processes. In this case, the organizational policies and procedure related to creating the WBS, as well as relevant project files and lessons learned from previous projects, are some examples of organizational process assets that can be helpful.
Furthermore, even though each project is unique, there are similarities among sets of projects in an organization. These similarities can be used to prepare templates that will be used as a starting point for the WBS, to avoid the duplication of work. With or without templates, you will need to go through breaking down the deliverables, a very important step in creating the WBS.
Decomposition
Decomposition is a technique used for subdividing the project deliverables into smaller, manageable tasks called work packages. The WBS is a hierarchical structure with work packages at the lowest level of each branch. Based on their complexity, different deliverables can have different levels of decomposition.
To understand Decomposition better, let us take a look at an example WBS of a Website Development Project
In any WBS – the lines are called “Branches” and the boxes are called “Nodes”. For practical understanding purposes, each of these nodes can be considered as one manageable piece of work.
As you can see, we have decomposed the whole project work into 3 parts:
1. User Interfaces
2. Server &
3. Database
Each of these parts is further divided into more nodes which carry out a specific function that is part of the higher level activity.
How do you decompose a Project Work?
You can decompose the project work by executing the following steps:
1. Identify the deliverables and the work involved by analyzing the project scope statement and the requirements documentation.
2. Understand the relationships among the deliverables.
3. Structure and organize the first level (Server, UI and Db in our example) of the WBS hierarchy. Based on the project at hand, you can use one of the following approaches:
o Use the deliverables as the components in the first level.
o Use the phases of the project as the components in the first level.
o Use the subprojects as components in the first level. A subproject is a part of the project that is independent enough of the rest of the project that it can be performed by another project team. This approach is useful when you want to outsource parts of the project.
o Use different approaches within each branch of the WBS, for example, a subproject and deliverables in the first level.
4. Decompose the upper level into more detailed components for the lower level.
5. Keep decomposing to lower levels until necessary and sufficient decomposition has been achieved.
6. Assign identification codes to the WBS components.
Trivia:
As the work is decomposed to lower levels of detail, work components become more concrete and manageable. However, you should avoid excessive decomposition, because it will lead to a large number of work packages, and it will not be possible to manage all of them effectively. In other words, excessive decomposition leads to inefficient use of management and other resources. Necessary and sufficient decomposition is the key.
During decomposition, the components are defined in terms of how the project work will actually be executed and controlled. You must verify the correctness of the decomposition at each level by verifying that the lower-level components are necessary and sufficient for the completion of the corresponding higher-level deliverables.
Trivia:
While using the technique of decomposition, remember a useful concept or trick: rolling wave planning. It’s a fancy term that refers to handling a deliverable or subproject that currently cannot be decomposed fully because you don’t know the details about it yet. For example, it is to be executed far into the future. You leave the decomposition of such a deliverable at a level allowed by the available information and wait for further decomposition until more information becomes available. Yes, you got it right. This is an example of progressive elaboration.
The WBS document is the key item of the Create WBS process, but there are some other output items as well.
Output of Creating WBS
The output of the Create WBS process consists of the following items:
Work breakdown structure
As explained earlier, the WBS is a deliverable-oriented hierarchical structure that decomposes the deliverables into the work that will be executed by the project team to create the planned deliverables and to accomplish the planned project objectives. The project manager creates this document with the help of the project team. Following are some important characteristics of the WBS:
• Control account - Remember that each node represents a deliverable or a component of it at certain level, and each deliverable will have scope, schedule, and cost attached to it. Some suitable nodes in the WBS are selected as management control points. At each of these control points, scope, schedule, and cost are integrated for the purposes of monitoring and controlling the performance. For example, the integrated scope, schedule, and actual cost at these points can be compared to the earned value to measure the project performance. Such management points are called control accounts. Each control account may have one or more work packages under it. Obviously, each work package must belong to only one account; otherwise, some factors, such as cost, will be double counted or counted multiple times. A WBS component that is below the control account, that has a well-defined work content but does not yet have a detailed schedule, is called a planning package.
• Code of account - Each component in the WBS hierarchy, including work packages, is assigned a unique identifier called a code of account identifier. These identifiers can then be used in estimating costs, scheduling, and assigning resources.
• Scope - The WBS embraces the full scope of the project. If a task is not included in the WBS, it will not be done as a part of the project.
• Step toward team building - Because the project manager creates the WBS with the help of the project team, it is also the beginning of the team-building process on the part of the project manager.
• Step toward scheduling - The WBS decomposes the project work into manageable pieces that can be assigned to individuals. This helps define the responsibilities for the team members and is the starting point for building the schedule.
• Reference for communication - Throughout the project, the WBS works as a reference for communication regarding what is included in the project and what is not.
WBS dictionary
This is a supporting document for the main WBS document to provide details about the components of the WBS. The details about a component might include elements such as a code of account identifier, description of work involved, quality requirements, acceptance criteria, a list of milestones schedule, cost estimates, required resources, contract information, and the organization or group responsible for this component.
Updates
During the create WBS process, the project team might realize that something out of the existing scope must be included in order to accomplish something in the scope. This will give rise to a change request, which might also come from other stakeholders during or after the first creation of the WBS. After the change request has been approved, not only the WBS will be changed—the scope statement must also be updated accordingly. The impact of the approved change request on the project scope management plan must be evaluated, and the plan must be updated accordingly.
Scope baseline
This is not a different item in and of itself. The scope statement, the WBS document, and the WBS dictionary combined constitute the scope baseline against which all the change requests will be evaluated.
Trivia:
Do not confuse the WBS with other information breakdown structures, such as the organizational breakdown structure (OBS), which provides a hierarchy of the performing organization and can be used to identify organizational units for assigning the WBS work packages. Remember, the end goal of the WBS is to specify the project scope in terms of work packages; this is what distinguishes the WBS from other information breakdown structures.
A Last Word:
You might be wondering who creates the WBS. Well, as expected, it is your responsibility, and you, the project manager have to create it with the help of your team.
Previous: Defining Project Scope
Next: Before & After the WBS
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
© 2013 by www.getpmpcertified.blogspot.com. All rights reserved. No part of this blog or its contents may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior written permission of the Author.
Followers
Popular Posts
-
So far, we have been talking in terms of projects only. There are two other terms that are closed linked with projects and project manageme...
-
In the previous chapter, we saw how to create the Project Scope Document. The next step in planning for a projects scope is to create the Wo...
-
In the previous chapter, we saw the project lifecycle in detail. In this chapter, we are going to take a look at the Project Management Kno...
-
In the previous chapter , we took a look at Expected Monetary Value or EMV Analysis . The Decision Tree Analysis is another tool/technique ...
-
In the previous chapter we learnt how to create the project human resource plan. To get resources you need to spend money (Cost) and you can...
-
In the previous chapter , we learnt the basic details about Continuous Distributions. In this chapter, we are going to take a detailed look...
-
In the previous chapter we learnt that the risk register is going to be constantly updated as we progress through the various processes in...
-
Expected Monetary Value Analysis or EMV Analysis in short is the 2nd tool and technique in the Quantitative Risk Analysis and Modeling Tech...
-
In the previous chapter, we saw that an organizations policies and culture can have a significant impact on a project. Towards the end we al...
-
In the previous chapter, we took a look at how to sequence the activities based on the requirements and dependencies. The next step would be...